The most commonly used CPU scheduling algorithms are First Come First Serve (FCFS), Shortest Job First (SJF), Round Robin (RR) and Priority
1. First Come First Serve Algorithm Scheduling Algorithm
In First Come First Serve algorithm the process that arrives first is allocated the CPU first. A queue is maintained in the RAM (ready queue) and the processes are allocated to the CPU as per their position in the queue i.e., the process first in the queue is allocated the CPU first.
Key Points of FCFS scheduling algorithm
- The job that arrives first is scheduled first
- Is non-preemptive algorithm
- Implemented using queue.
- Suffers from Convoy effect.
PPT on FCFS scheduling algorithm
Video on FCFS scheduling algorithm
2. Shortest Job First (SJF) scheduling algorithm
In shortest job first scheduling algorithm the process with the least burst time is allocated the CPU first. Shortest job first is of two types:
1. Non – Preemtive (NP)
2. Preemptive (also known as Shortest Remaining Time First(SRTF)
2.1 Shortest Job First (Non Preemptive) scheduling algorithm
In SJF(NP) once a process gets the CPU, it releases the CPU only when the burst time is over. The decision of the shortest job is made out of those process which are in the ready queue at any given time thus, keep an eye on the arrival time (else you may get the answer wrong).
PPT on SJF(NP) scheduling algorithm
Video on SJF(NP) scheduling algorithm
2.2 Shortest Job First (Preemptive) scheduling algorithm
- While a process is running if a process with lower burst time arrives then it will pre-empt the currently running process.
- Whenever a new process arrives check whether its burst time is less than the remaining burst of currently running process
PPT on SJF(P) scheduling algorithm
Video on SJF(P) scheduling algorithm
3. Priority Scheduling algorithm
- In priority scheduling a number is assigned to each process which indicates its priority level.
- Lower the number, higher is the priority.
3.1 Priority Scheduling (Non-Preemptive) algorithm
PPT on Priority Scheduling (NP)
Video on Priority Scheduling (NP)
3.2 Priority Scheduling (Preemptive) algorithm
PPT on Priority Scheduling (Preemptive)
Video on Priority Scheduling
Issue with Priority scheduling algorithm
Starvation – Priority scheduling can lead to starvation
Solution- Solution to the starvation problem is Aging. In aging the priority of a process is increased by one unit after a fixed interval of time. In this way the process will have the highest priority after fixed interval of time and then it is sure to get the CPU.
4. Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm
- Is pre-emptive algorithm
- The CPU is shifted to next process after fixed interval of time called time quantum.
- The process that is preempted is added to the end of the queue.
PPT on Round Robin scheduling algorithm
Video On Round Robin scheduling algorithm
5. Multilevel Scheduling Algorithm
In multilevel scheduling process are divided into groups and each group is assigned a separate queue. Each queue can have a separate scheduling algorithm. The queues themselves are also scheduled. For example, there can be different queues for foreground processes and background processes. The processes in foreground queue can be scheduled using FCFS while the queue containing background processes can be scheduled using SJF(P).
PPT on Multilevel Scheduling Algorithm
Previous Next CPU Scheduling Race Condition

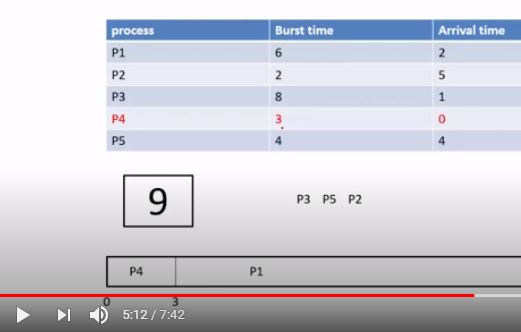

Priority Scheduling Non-Preemptive
AWT = 6
ATT = 19.8
Priority scheduling Non-preemptive:
Awt= 6
Att= 19.8
Priority scheduling non preemptive
Q1 a) Att=10.6