In this post we will learn how to define variables in shell script. A variable is used to store any value. The value can be an integer, float, character or even a string. There is not need to write the data type as is the case with C or C++ languages. For example
x=1 y=2.5 name="Your name"
are all valid variable definitions. Also, there is no need to specify the data type. The shell will take care of it automatically. The general syntax is:
variable=value
Valid Variable Name in shell script
A variable name must start with a character(A-Za-z) or an Underscore(_) then there can be any number of characters, digits(0-9) or underscore.
Some examples of valid variable names are
Name sum1 _Count23 A_B_2
Some examples of invalid variable names are
123 1ABC @CB Abc*df
Accessing value of a Variable
To get/use the value of a variable ‘$’ sign is used. For example
Name="Robert Junior" echo "Value of variable Name is $Name"
Run the above script as:
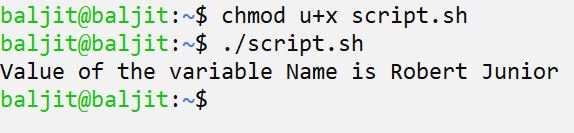
How to assign filename to a variable in shell?
The method to assign a filename to a variable is similar as above. Now, there can be two situations. One, you already know the filename. For example there is a file “F1.txt”. So, simple write
f_name=F1.txt
Second, if you want to store the name entered by the user in a variable
echo "Enter filename" read f_name
Now, when the user runs the script and enters the filename, it gets stored in the variable f_name.
Difference between using Double Quotes (“) and Single Quotes (‘)
Suppose that you the variable name is Name. In the output you want the statement to contain the word $Name. Now, how can you do this?
Name=Robert echo "Value of $Name is $Name"
The output will be:
Value of Robert is Robert
But, what we want is
Value of $Name is Robert
To achieve this use Single Quotes a shown below:
Name="Robert" echo Value of '$Name' is $Name
This time the output will be as expected that is,
Value of $Name is Robert