What is Stratis?
Stratis is a Linux-based local storage management system. It focuses on simplicity and ease of use while providing advanced storage capabilities.
The following tasks are made easier with Stratis:
- Storage setup at the start
- Changing things afterwards
- Making use of enhanced storage options
Stratis is a local storage management system that enables extensive storage features and is a hybrid user-kernel system. A storage pool sits at the heart of Stratis. This pool is made up of one or more local disks or partitions, and the pool is used to build volumes.
Many beneficial functions are available through the pool, including:
- Snapshot
- Thin provisioning
- Tiering
Stratis Components
There are three components that you need to understand before using stratis
blockdev
Refers to the block devices such as disks or partitions that will be used for storage. Other block devices which can be used with Stratis are:
- LUKS
- LVM logical volumes
- MD RAID
- DM Multipath
- iSCSI
- HDDs and SSDs
- NVMe devices
pool
One or more block devices make up a pool. The pool’s total size is equal to the total number of block devices. Stratis creates a /dev/stratis/my-pool/ directory for each pool.
filesystem
A filesystem is a thinly provisioned layer that does not have a predetermined overall size. As data is added, the filesystem’s true size expands. As the size of the data approaches the virtual size of the file system, Stratis automatically expands the filesystem.
Now let’s learn How to use Stratis to manage storage in RHEL8
Using Stratis
As a pre-requisite, you need to have one or more block devices. So make sure you have at least one free. Refer to these posts to learn how to add block devices or how to create disk partitions or use LVM (Logical Volume Management).
Step1: Installing packages
First, You need to install two packages: startisd and stratis-cli
#yum install stratisd stratis-cli Step2: Start and enable startis
#systemctl start stratisd
#systemctl enable stratisdStep3: Create a stratis pool from the block devices.
I will use /dev/sdg disk to create the pool using the stratis pool create command. Make sure that the size of the disk is at least 1GB. In order to view the existing pools use stratis pool list command.

To create a pool from multiple devices, separate the list of devices with space
#stratis pool create <Pool name> <device1> <device2> <devicen>Step4: Create a filesystem from the pool
Use the stratis fs create command to create a file system from the existing pool. Remember no need to specify the file system type as the default type is xfs. We create two filesystems NewFS and NewFS1. Use stratis fs list to view all the created file systems.
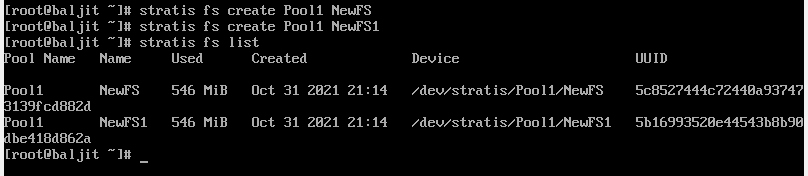
Step5: Create a mount point to mount the filesystem
$mkdir /mountFSStep6: Mount the filesystem persistently
Open the /etc/fstab file and make the following entry. In this case you need to specify the UUID of the file system that you want to mount permanently. To view the UUID use the stratis fs list command
UUID=5c8527444c72440a937473139fcd8824 /mountFS xfs defaults,x-systemd.requires=stratisd.service 0 0
Finally, mount using
#mount -aDeleting a Stratis Filesystem
Before deleting a stratis filesystem unmount it
#umount /mountFS
Next use the stratis filesystem destroy command to delete one of the filesystems (NewFS in this case)

Deleting a Stratis Pool
To delete a stratis pool use the stratis pool destroy command as below.

Adding disk to a Stratis Pool
To increase the space in the stratis pool we can add another disk to the existing pool. In order to add a disk use the stratis pool add-data command

Video on How to use Stratis to manage storage in RHEL8
