Banker’s Algorithm – is a technique used for deadlock avoidance when there are multiple instances of a resource.
Important Points:
- Can be used only when multiple instances exists.
- Every process
- Tells the max. no. of instances of any resource it requires
- The maximum need can not exceed the total number of resources in the system.
- On every request the system determines whether granting that request will leave the system in safe state or not.
- Data structures required
- Available – no. of available resources of each type
- Max – maximum need of any process for any resource
- Allocation – number of resources allocated to each process
- Need – (Max – Allocation)
Banker’s Algorithm Implementation
This algorithm requires four data structures to be implemented:
- Available – no. of available resources of each type with the system.
- Max – maximum need of any process for any resource
- Allocation – number of resources allocated to each process
- Need – is calculated based on the formula (Max – Allocation)
Safety Algorithm [1]
- Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n, respectively.
Initialize:
Work = Available
Finish [i] = false for i =0,1,2,3, …, n. - Find an i such that both:
(a) Finish [i] = false
(b) Needi <= Work
If no such i exists, go to step 4. - Work = Work + Allocationi
Finish[i] = true
go to step 2. - If Finish [i] == true for all i, then the system is in a safe state
Request Algorithm [1]
Request = request vector for process Pi. If Requesti [j] = k then
process Pi wants k instances of resource type Rj.
- If Requesti <= Needi go to step 2. Otherwise, raise error condition,
since process has exceeded its maximum claim. - If Requesti <= Available, go to step 3. Otherwise Pi must wait, since
resources are not available. - Pretend to allocate requested resources to Pi by modifying the state
as follows:
Available= Available – Requesti;
Allocationi = Allocationi + Requesti;
Needi = Needi – Requesti;;
• If safe => the resources are allocated to Pi.
• If unsafe => Pi must wait, and the old resource-allocation state
is restored
PPT on Banker’s Algorithm
Note: Clicking on the “next” slide button will not display any animation. Hence, Click within the slide area for animations.
Example of Banker’s Algorithm
Q. Consider a system with five processes Po through P4 and three resource types A, B, and C. Resource type A has 10 instances, resource type B has 5 instances, and resource type C has 7 instances. Suppose that, at time T0 , the following snapshot of the system has been taken:
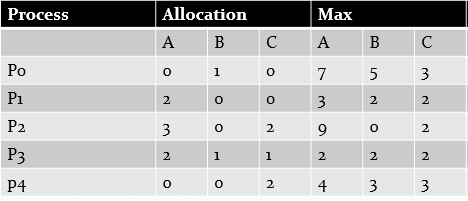
Solution:
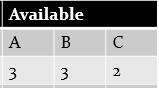
Available instaces of A = Total – Allocated = 10 – (0+2+3+2+0) = 3
Similarly, Available instaces of B = Total – Allocated = 5 – (1+0+0+1+0) = 3
Finally, Available instaces of C = Total – Allocated = 7 – (0+0+2+1+2) = 2
Next, Calculate Need by using the formula
Need = Max – Allocation
………………………A B C
Need for P0 = 7 4 3
Hence, the entire scenario looks like

Now find out any process whose Need can be satisfied with Available. P1 is one such process. So, Add P1 to safe sequence <P1>.
Update the Available by using formula
Available = Available + Allocation of process added to safe sequence (P1)
So, new Available is 5 3 2
Next, find out another process whose Need is less than the updated Available i.e., 5 3 2.
P3 is one such process. Hence, Add P3 to safe sequence <P1, P3>.
Now, Update Available by adding Allocation of P3 to current Available.
Proceed in the same manner. If all the process can be added to the safe sequence then the system is in safe state otherwise not.
Practice Question on Banker’s Algorithm
Q1. Consider a system with four processes Po through P3 and four resource types A, B, C and D. Resource type A has 6 instances, resource type B has 9 instances, resource type C has 6 instances, and D has 9 instances. Suppose that, at time T0 , the following snapshot of the system has been taken:

Is the system in safe state or not?
Can a request of P3 for <1,1,1,1> be granted?
[1]Galvin, P. B., Gagne, G., & Silberschatz, A. Operating system concepts. John Wiley & Sons, 8th Edition
Previous Next Resource Allocation Graph Deadlock Detection and Recovery


yes sir… it is safe
Safe sequence